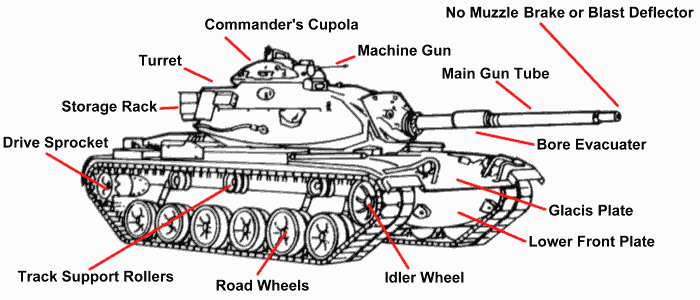
There are four structural areas that can be used to identify vehicles: Suspension system, turret, main gun, and commander's station.
Most armored vehicles have all four areas of characteristics, though not all vehicles do.
Reactive armor, camouflage, and increased use of sandbags can greatly alter the shape of vehicles.
-
Suspension system.
This is the least reliable area for identification as it is often concealed by vegetation or by terrain.
Characteristics of the suspension system that can be used to distinguish combat vehicles are:
- Tracked vehicle.
- Number of road wheels.
- Spacing between road wheels.
- Number of support rollers.
- Armored skirt.
Most NATO vehicles include a suspended track, support or return rollers, torsion bars, evenly spaced road wheels, and shock absorbers.
Most Warsaw Pact vehicles include a flat suspension system, no support or return rollers, no torsion bars, unevenly spaced road wheels.
- Wheeled vehicle.
- Number of tires.
- Spacing between tires.
-
Turret.
Characteristics of the turret that can be used to distinguish vehicles are:
- Position on the hull: well forward, center, or to the rear.
- Shape of turret: rounded, elongated, or boxy.
- Presence, absence, or location of searchlight.
- Externally mounted storage racks and other equipment.
-
Main gun.
Armament varies from machine guns to large cannons. In turreted vehicles, normally the heaviest armament is in the turret.
Main gun identification features include:
- The presence and location along the gun tube of a bore evacuator.
- The presence of a muzzle brake or blast deflector. Types of muzzle brakes:
- Single baffle.
- Double baffle.
- Multi-baffle.
- The presence or absence of a thermal jacket.
-
Commander's station.
This is usually a simple hatch or a cupola. A cupola is a small turret-like projection on the top of the turret that houses the
commander's station, either on the right or left side. A cupola usually mounts a machine gun.