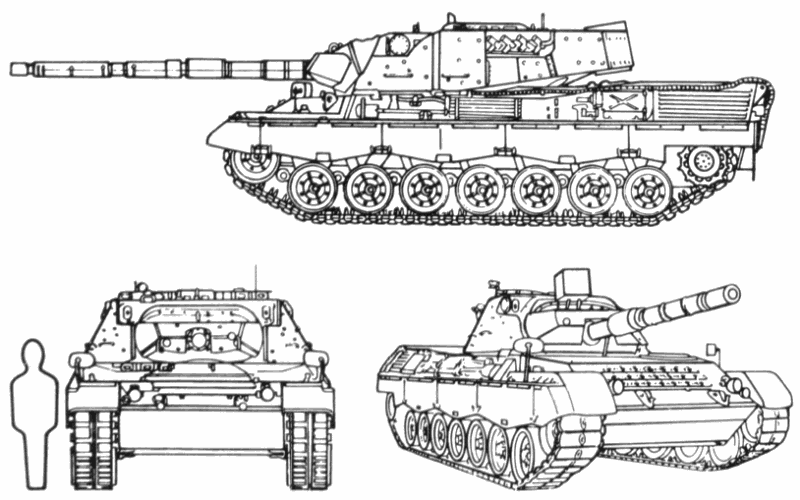
The Leopard 1 was developed by West Germany and has been exported in several versions to several armies in the world.
The hull has two compartments.
The engine is at the rear and separated from the crew by a fireproof bulkhead.
The driver is in the front on the right and has a hatch cover opening to the left.
In front of his hatch are three periscopes, one that can be infrared or image-intensification for night driving.
The commander and gunner sit on the right and the loader on the left of an all-cast turret.
Hatch covers open to the rear for both the commander and gunner.
Eight periscopes for all-round observation are provided for the commander.
Sights and one periscope are at the gunner's station, while the loader has two periscopes.
In the turret roof in front of the commander's hatch is a swivel-mounted x6 to x20 zoom periscope.
The gunner, seated in front of and below the commander, has a rangefinder and a telescope mounted coaxially with the main gun.
On the left side of the turret is an ammunition resupply hatch.
Many models have a stowage basket at the turret rear.
A searchlight sits over the main gun, but is sometimes removed and stowed at the back of the turret.
The infrared range is 1,200 meters and the white light range is 1,500 meters.
A low-light-level television (LLLTV) observation and sighting system is on the Leopard 1A1A2.
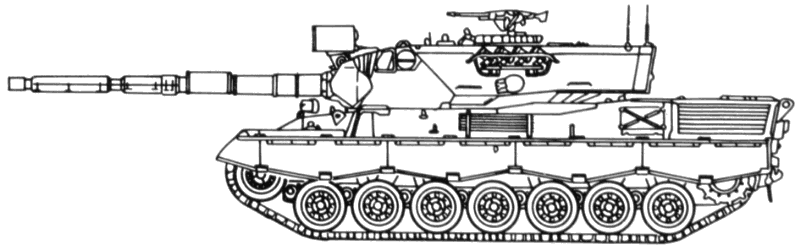
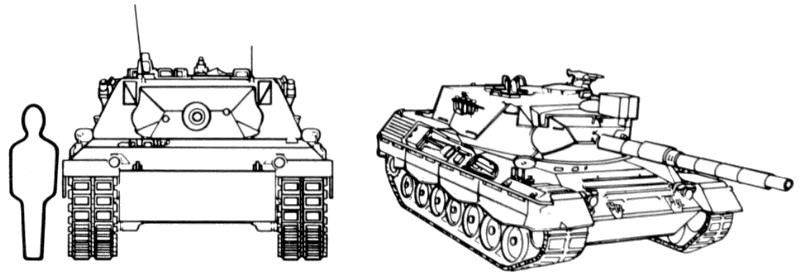
Recognition features:
- Supported, fully tracked, three support rollers.
- Seven evenly spaced, pressed road wheels.
- Jagged or wavy design track skirting.
- One 105mm gun with no muzzle brake.
- Bore evacuator two-thirds the distance from the muzzle.
- Large wedge-shaped gun mantle.
- Gun may have a thermal shroud.
- One 7.62mm machine gun mounted coaxially with the main gun.
- One 7.62mm machine gun mounted on the turret roof.
- Elongated or oval, slab-type, all-cast turret mounted forward of center.
- Turret has an external stowage basket in the rear.
- Sides of the hull slope upward toward the center.
- Sloped front armor.
- Upper and lower glacis form a straight edge.
- Louvered exhaust grills on the rear of the hull sides.
- Engine plate in the rear angles up the from the turret.
- One rectangular louvered engine vent on each side at the rear.
- One "postage stamp" engine vent centered on the rear deck.
- One rounded and one oval hatch in line on the turret.
- Driver's hatch on the front deck at the right of the gun tube.
- Box-shaped searchlight (if mounted) above and to the left of the gun.
- Leopard 1A2s have round turrets.
- Leopard 1A3s and 1A4s have angular, box-shaped turrets.
More than a dozen fire control systems, many with thermal sights, are available for this tank.
Improved stabilization systems include US HR Textron, French SAMM, and German FWM.
Other options include a front mounted dozer blade, improved air conditioning, and a 120mm smoothbore gun.
A variety of systems use Leopard 1 chassis. These include Gepard air defense gun, engineer and recovery vehicles, and a bridgelayer.
- Leopard 1
- 1965. Original production model with original tracks, and without track skirts, stabilization or thermal sleeve for gun.
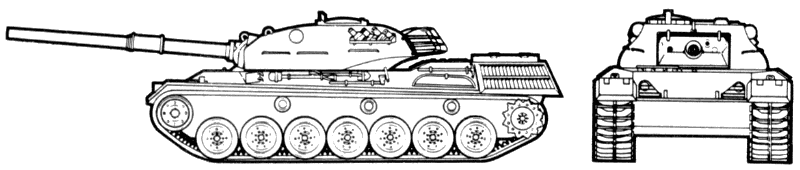
- Leopard 1A1
- Many of the Leopard 1s became the Leopard 1A1 when fitted with a main gun thermal sleeve, stabilization system, and new tracks and skirts.
The stabilization system gives a higher first-round hit probability by controlling elevation and traverse to acquire and engage the target while moving across country.
See data above.
- Leopard 1A1A1
- Fitted with additional armor made of rubber-lined steel plates screwed on the turret, gun shield, and turret bustle back.
More steel plates were welded on the sloped front roof section.
- Leopard 1A1A2
- A version with low-light-level television (LLLTV) sights.
- Leopard 1A2
- This version has a stronger cast steel turret, an improved NBC system, air conditioning, and image-intensification night vision for the commander and driver.
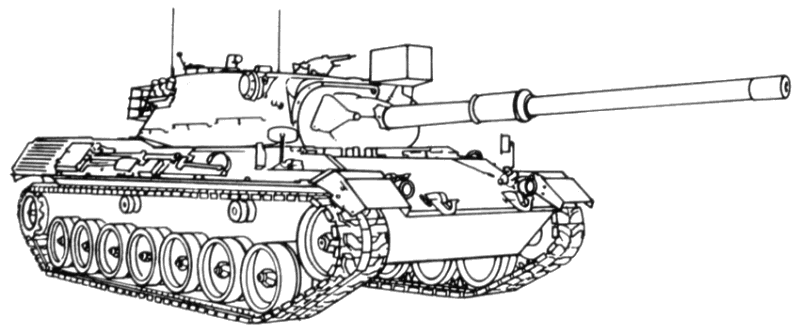
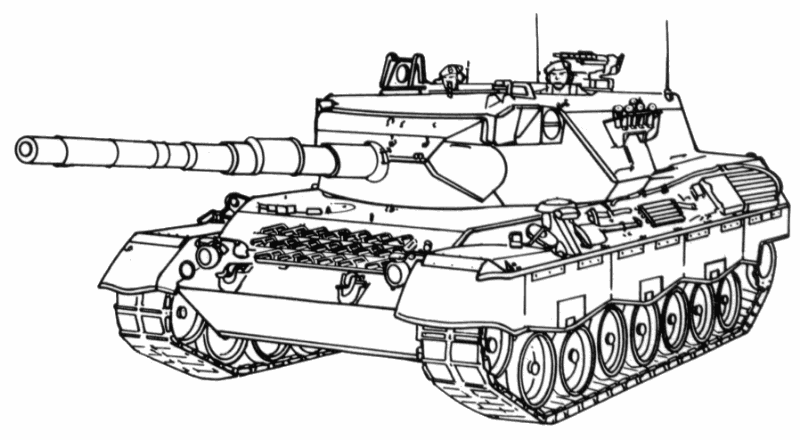
- Leopard 1A3
- Incorporates a new welded turret with a wedge-shaped mantlet.
A contoured rear turret stowage bin holds the searchlight when it is not mounted over the main gun.
The loader's periscope is movable in elevation and azimuth.

Left rear view of German Leopard 1A3
14-NOV-1984.
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x713, 235K, JPEG
- Leopard 1A4
- Final German Army production system.
This version has an integrated fire control system consisting of a commander's stabilized panoramic telescope and a gunner's primary sight with stereoscopic rangefinder coupled to a fully-stabilized main gun and ballistic computer.
- Leopard 1A5
- 1A1/1A2 tanks refitted with an EMES-18 FCS and thermal sights.
- Australian Leopards (Leopard AS1)
- The Australian Leopards are the 1A3 model fitted with the Belgian SABCA fire control system and a tropical kit.
Leopards replaced the Centurions in the 1st Royal Australian Armoured Regiment.

1st Armoured Regiment (1ARMD)
Exercise Talisman Saber 2005
25-JUN-2005.
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x768, 253K, JPEG

1st Armoured Regiment (1ARMD)
Exercise Tandem Thrust 2001
U.S. Navy Photo
2000x1312, 232K, JPEG
- Belgian Leopards (Leopard 1 BE, Leopard 1A5 BE)
- The Belgian vehicles had their MG3 machine guns replaced by FN 7.62mm weapons and some minor storage changes.
Belgian Leopard 1A5 BE tanks are upgraded 1A1/1A2s, with new FCS, FN MAG 7.62mm machine guns, and thermal sights.
- Canadian Leopards (Leopard C1, Leopard C2)
- Leopard C1 - The Canadians selected a modified version of the Leopard 1A3 fitted with the Belgian fire control system to replace their Centurion tanks.
Leopard C2 - An upgraded Leopard 1A5 which features a fully stabilized digital fire control system with an integrated thermal imaging system and laser range-finder, and can be fitted with add-on armor.

Canadian Army Leopard C2.
- Greek Leopards
- The Greek Leopards have the EMES 12A3 fire control system and an LLLTV system.
- Italian Leopards (Leopard 1A2, Leopard 1A5)
- The Italian 1A2 was upgraded with Sirio thermal FCS, gun stabilization, and turret drive.

Italian Army Leopard 1A5.
- Netherlands Leopards (Leopard 1-V)
- The Dutch Leopards have the EMES-12A3 FCS, PZB II night sight, different radios, Dutch type smoke dischargers, and three stowage panniers.
They are fitted with the same applique turret armor as is on the Leopard 1A1A1.
The Dutch Leopards use the British L52 APDS round for the main gun.
- Norwegian Leopards
- Like the Netherlands, the Norwegians use the British L52 APDS round.
All Norwegian Leopards are being upgraded to Leopard 1A3 standards, but will retain the cast turret.

Exercise Alloy Express
05-MAR-1982.
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x768, 174K, JPEG

Exercise Cold Winter '87
01-MAR-1987.
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x745, 262K, JPEG

Leopard 1A1A1
Exercise Teamwork '88
01-SEP-1988.
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x674, 284K, JPEG
- Turkish Leopards (Leopard 1 TU, Leopard T1)
- The Turkish Leopards are 1A3s with the EMES 12A3 fire control system and an LLLTV system.
- Leopard Armored Recovery Vehicle (ARV)
- The ARV has a tank chassis with a new hull.
Standard equipment is a dozer blade, hydraulic crane pivoted on the front right of the hull, a 35-ton winch, electric winch, and welding system.
With a crew of four, the ARV recovers and tows damaged or disabled vehicles.
It can lift complete vehicles or components up to 20 tons.
It carries a spare powerpack, dozing equipment, and refueling equipment.
The ARV is armed with two 7.62mm machine guns, one for anti-aircraft defense, and smoke dischargers.

Italian Army Leopard ARV.

Canadian Army Leopard ARV, the "Badger."
- Leopard Armored Engineer Vehicle (AEV)
-
The AEV is based on the ARV.
The only differences are that the AEV has a heat exchanger, explosives are carried for demolition work, an auger is carried in place of the spare powerpack on the rear, and the dozer blade can be fitted with scarifiers.

Italian Army Leopard AEV.

Canadian Army Leopard AEV, the "Taurus."
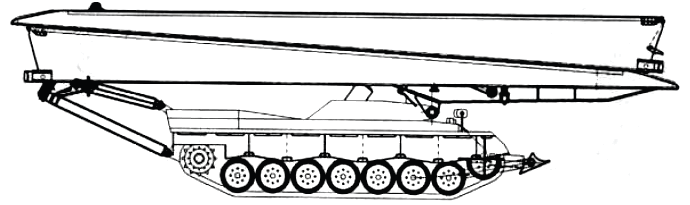
- Leopard Biber (Beaver) Armored Vehicle Bridge Launcher (AVLB)
-
The Leopard AVLB is a fixed span bridge mounted on a Leopard I tank chassis, using a horizontal launch system instead of the more common scissors launch.
The bridge provides an MLC 60 gap-crossing capability for gaps up to 21 meters using prepared abutments or 20 meters using natural banks.
It operates with a crew of two, with launching and retrieval times of less than 5 minutes.
It has eight launcher tubes that can use smoke rounds to conceal bridge launching or canister-type high explosives (HE) grenades for self defense.
Used by Australia, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Italy, the Netherlands, and Norway.

Italian Army Leopard AVLB.

Canadian Army Leopard AVLB, the "Beaver."
- MAN Leopard 1 LEGUAN Armored Vehicle-Launched Bridge (AVLB)
-
The MAN Leopard 1 LEGUAN AVLB is based on the hull and chassis of the Leopard 1 MBT with all main and subcomponents unchanged.
Various items from the removed turret and other components have been modernized and integrated into the AVLB.
The 26-meter, aluminum alloy bridge follows standard construction design.
Before laying the bridge, a hydraulically operated tilt-table support blade is lowered under driver control from the front of the hull.
Acting as a stabilizer blade it can also be used for light obstacle clearance.
Operating with a crew of two, launching and retrieval times are less than 5 minutes.
Currently in service with Norway and on order for Belgium.