The T-62 MBT was developed from earlier T-54/T-55s.
However, the T-62 has a longer and wider hull, different spacing on the road wheels (a distinct gap is located between the third and fourth and fourth and fifth road wheels.), different turret shape, and a longer and fatter gun barrel with a fume extractor towards its muzzle.
The T-62 has an all-welded hull divided into three main compartments with the driver at the front, fighting compartment in the center, and the engine and transmission at the rear.
The T-62 has a four-man crew consisting of the tank commander, driver, gunner and loader. The tank commander is seated on the left and the driver is seated in the front of the vehicle on the left side.
The T-62 also has smoke-laying capabilities.
The turrets of older former Soviet Union tanks rotate much slower than those on US and NATO tanks.
It takes more than 21 seconds for T-60-series tank turrets to rotate through a full 360°.
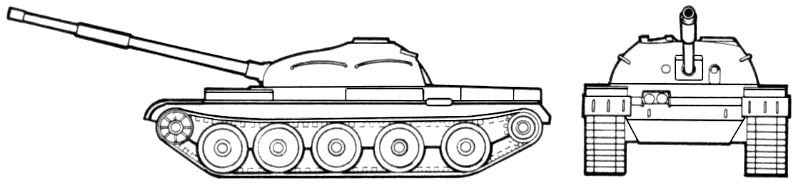
Recognition features:
- Five twin rubber-tired road wheels on each side with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and no track return rollers. A hydraulic shock absorber is also provided at the first and last road wheel stations.
- Three external diesel fuel tanks on the right side and a single auxiliary oil tank on the left side. The T-62 also has two optional drum-type fuel tanks that can be fitted on the rear of the vehicle for an increased operational range.
- An unditching beam mounted at the hull rear.
- Two snorkels, a thin one for operational use and a large diameter one for training. The operational snorkel is disassembled and carried at the turret's rear when not in use.
- A longer hull and gun tube than the T-54/T-55.
- A rounded turret (view from side).
- A low-silhouetted hull.
- A commander's cupola that is further back on the turret than the loader's hatch. The cupola has four periscopes; two in the hatch cover and two in the forward part of his cupola.
- A driver's single-piece hatch cover.
- Two periscopes for the gunner, one of which is used in conjunction with the main searchlight mounted coaxially to the right of the main armament.
- A loader's single hatch cover to the right of the turret with a periscope that can be used to the front or rear.
- A straight splash plate mounted on the front of the vehicle with a white light and an infrared headlamp mounted to the rear of the deflector.
- Front-climbing curved handles on the turret.
- Turret rails for infantry or personal equipment.
- A box-like radiation detector/actuator mounted on the right side of the turret behind the compressed air tanks.
- A blower mounted at the rear of the turret to the left of the spent cartridge ejection door.
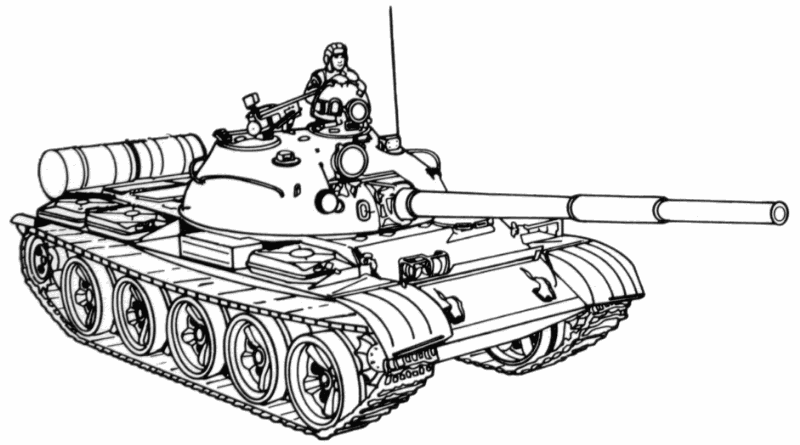
Optional sights and fire control systems include the Israeli El-Op Red Tiger and Matador FCS, Swedish NobelTech T-series sight,
and German Atlas MOLF. The British Marconi Digital FCS, South African Tiger, and Belgian SABCA Titan offer upgraded function.
One of the best is the Slovenian EFCS-3 integrated FCS.
A variety of thermal sights are available. They include the Russian Agava, French SAGEM-produced ALIS and Namut sight from Peleng. There are
thermal sights available for installation which permit night launch of ATGMs.
Other improvements available include a hull bottom reinforced against mines, rubber track pads, and a thermal sleeve for the gun.
A number of T-62 tanks have been fitted with additional armor protection for the fuel tanks, above the road wheels, glacis plate, and each side of the 115mm gun halfway round the turret.
The additional turret armor is fitted passively to the turret.
Some T-62 tanks were fitted with missile launchers on the rear of the turret for air defense, but it is not known if these were ever deployed operationally.
T-62 main armament modifications include:
- A 105mm L7 rifled tank gun replaces the standard 115-mm U-5TS gun.
- A GIAT 120-mm smoothbore gun replaces the 115-mm gun.
The T-62 can be fitted with mine-clearing equipment like that fitted to the T-54/T-55.
T-62 variants with a V-46 T-72-type engine add -1 to their designation.
- T-62
- Original production model. Recognition features:
- Fully tracked.
- Five road wheels (greater spacing between third and fourth, and fourth and fifth road wheels) with no support rollers.
- Dome-shaped turret over third road wheel.
- Flat, low-silhouetted hull.
- Bore evacuator 1/3 way from muzzle.
- Curved front infantry handrail.
- T-62A
-
Added a 12.7-mm DShK machine gun to loader's cupola.
- T-62D
- Variant with the Drozd Active Protective System (APS) vs Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA).
- T-62M
-
See data above. Added protection, fire control system (FCS), and anti-tank guided missile capability.
The T-62M's 1K13 sight is both night sight and ATGM launcher sight; however, it cannot be used for both functions simultaneously.
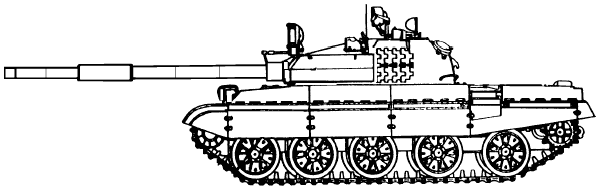
- T-62M1
- Variant with Volna FCS but no missile launch capability.
- T-62MK
- Command variant. Includes additional internal communications and navigation systems.
- T-62MV
- Version with ERA in place of the bra armor. The ERA includes Kontakt ERA and Kontakt-5 2nd-Generation ERA.
- T-62 (Egyptian)
- Some of these T-62s are fitted with Sakr ground-to-ground smoke rocket launchers.
British Royal Ordnance has provided substantial quantities of 115mm tank barrels to Egypt for replacement of the existing T-62 115-mm U-5TS guns.
- TO-62 Flamethrower
- The TO-62 flamethrower is in CIS service. The flame gun has an effective range of 100 meters and is mounted coaxially with the 115mm gun.
- M1977 Armored Recovery Vehicle (ARV)
- These ARVs are limited to towing operations and as far as it known, they are not fitted with winches or other specialized recovery equipment.
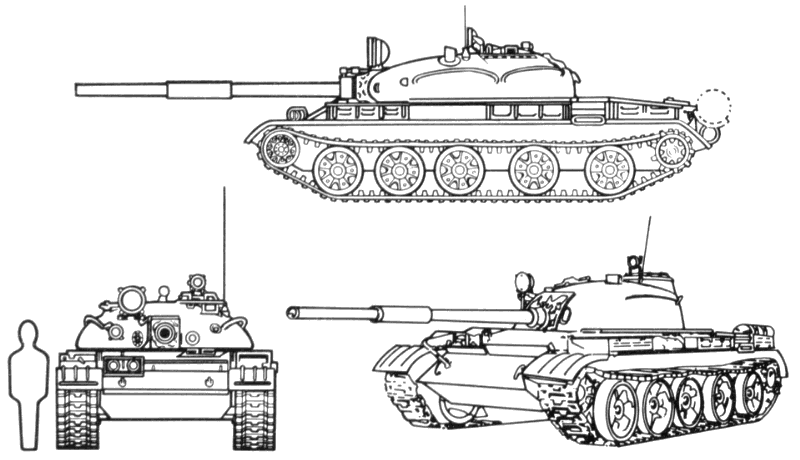
 Recognition features:
Recognition features:

