A
- AA
- anti-aircraft, antiaircraft
- AAAV
- advanced amphibious assault vehicle
- abatis
- An obstacle created by felling trees so that the trunks lie across a road or trail and impede movement.
- ACE
- armored combat earthmover (vehicle)
- ACV
- air cushion vehicle
- active guidance
- Guidance by which a missile, warhead, or projectile emits radiation (electromagnetic) and
homes in on the signal reflected from a selected target.
- active terminal guidance (or homing)
- A method of guidance in which energy is transmitted from the round
and guidance information is derived from reflected or scattering of that energy by a target. Varieties of active
guidance current in military use or development include radar, ladar, and active acoustics for undersea weapons.
- AD
- air defense
- ADA
- air defense artillery
- ADAM
- area denial artillery munitions
- AEW
- aircraft early warning
- AGL
- automatic grenade launcher
- AI
- artificial intelligence
- airburst
- (1) An explosion of a bomb or projectile above the surface as distinguished from an explosion on impact or after penetration of the surface.
- (2) A nuclear detonation in the air at a height of burst greater than the maximum radius of the fireball.
- AM
- (1) amplitude modulation
- (2) antimaterial
- ammo
- ammunition
- amphibious vehicle
- An automotive vehicle or chassis which embodies all-wheel drive, is equipped to meet
special military requirements, and which has sealed electrical systems or adaptation features for deep-water fording. (
- AMRAAM
- advanced medium-range air-to-air missile
- AP
- (1) antipersonnel
- (2) armor piercing: Ammunition, bombs, bullets, projectiles, or the like which are designed to penetrate armor and other resistant targets.
- (3) ammonium perchlorate
- APB
- antimatter particle beam
- APC
- armored personnel carrier (vehicle)
- APDS
- armor-piercing, discarding sabot (ammunition)
- APDS-T
- armor-piercing discarding sabot with tracer (ammunition)
- APE
- armor-piercing explosive (ammunition)
- APFSDS-T
- armor-piercing, fin-stabilized discarding sabot with tracer (ammunition)
- APERS
- antipersonnel
- API-T
- armor-piercing incendiary tracer (ammunition)
- APICM
- antipersonnel improved conventional munitions
- acquisition range
- sensor range against a category of targets. Targets are usually categorized as infantry, armored vehicles,
or aircraft. Acquisition includes four types (or levels of clarity, in ascending order of clarity): detection, classification,
recognition, and identification. Where the type of acquisition is not specified, the acquisition range will be regarded as sufficient
for accurate targeting. This range is comparable to the former Soviet term sighting range.
- ARDEC
- (U.S.) Army Research, Development, and Engineering Center
- arming range
- The range at which a fuze becomes operational.
- armor
- Any physical protective covering used on vehicles or persons to defeat projectiles or fragments.
- ASCM
- antiship cruise missile
- ASW
- antisubmarine warfare
- AT
- anti-tank, antitank
- ATACMS
- Army tactical missile system
- ATAS
- air-to-air Stinger (missile)
- ATF
- automatic terrain following
- ATGM
- anti-tank guided missile
- AUV
- (1) autonomous underwater vehicle
- (2) autonomous unmanned vehicle
- AVLB
- armored vehicle-launched bridge
- AWACS
- airborne warning and control system
- azimuth
- A horizontal, clockwise angle measured from north. A grid azimuth, measured from grid north, is the azimuth
normally used in the field artillery. A magnetic azimuth is measured from magnetic north; a true azimuth is measured from true north.
B
- ballistic missile
- Any missile which does not rely upon aerodynamic surfaces to produce lift and
consequently follows a ballistic trajectory when thrust is terminated.
- barrel
- a metal tube through which ammunition is fired, which controls the initial direction of the projectile
- BCIS
- battlefield combat identification system
- BDA
- battle damage assessment
- bde
- brigade
- beam-rider guidance
- Radar guidance system in which the vehicle being guided continuously senses, and
corrects for, deviation from center of coded radar or laser beam which is usually locked onto target. Accuracy
degrades with distances from emitter.
- beehive
- A type of antipersonnel ammunition designed for use in defending a position against massed personnel attack.
- BFV
- Bradley (infantry) fighting vehicle
- binary chemical munition
- A munition in which chemical substances, held in separate containers, react when
mixed or combined as a result of being fired, launched, or otherwise initiated to produce a chemical agent.
- BIT
- built-in test
- blank ammo
- Ammunition that does not contain a projectile but does contain a charge of low explosive, such as black powder, to make a noise.
- BLOS
- beyond line-of-sight
- BMD
- ballistic missile defense
- BMP
- A light armored vehicle made by the former Soviet Union.
- bn
- battalion
- bourrelet
- A raised metal or plastic ring around the outer forward surface of the projectile. Its purpose is to center the forward part of the projectile as it travels through the bore.
- BRDM
- A scout car made by the former Soviet Union.
- breechblock
- A movable steel block that closes the breech of a cannon.
- brilliant munition
- A "many-on-many" munition that operates autonomously to search for, detect,
identify, acquire, and attack specific classes of targets. The sensor on each munition acquires and attacks only one
among the class of targets, so that in a battlefield situation two munitions do not attack the same target, thus
leaving others inviolate.
- BSFV
- Bradley Stinger (missile) fighting vehicle
- BTR
- A light armored vehicle made by the former Soviet Union.
- burster
- An explosive charge used to break open and spread the contents of chemical projectiles, bombs, or mines.
C
- C2
- command and control
- C3
- C³
- command, control, and communications
- C3I
- command, control, communications, and intelligence
- CAG
- carrier aircraft group
- cal
- caliber
- caliber
- (1) The inside diameter of the tube as measured between opposite lands. A .45 caliber pistol has a barrel with a diameter of 45/100 of an inch
- (2) The diameter of a projectile.
- (3) An expression of the length of the tube obtained by dividing the length from the breach face to the muzzle by the inside diameter of its bore. A gun tube with a bore 40 feet long (480 inches) and 12 inches in diameter is 40 calibers long.
- CAP
- combat air patrol
- CARC
- chemical agent resistant coating
- CAS
- close air support
- CBU
- cluster bomb unit
- CCM
- counter-countermeasures
- CE
- chemical energy: The class of ammunition which employs a shaped charge for the lethal mechanism. Ammunition types which employ CE include HEAT and HESH.
- CEP
- Circular error probable or circle of equal probability. A measure of accuracy at a specific range,
expressed in terms of the radius of the circle, centered on the target, in which 50 percent of the payloads impact.
- CEV
- combat engineer vehicle
- CFV
- cavalry fighting vehicle
- chemical agent
- A chemical compound which produces incapacitating, lethal, or damaging affects on man, animals, plants, or materials.
- CITV
- commander's independent thermal viewer
- CIV
- commander's independent viewer
- CLGP
- cannon-launched guided projectile
- CLOS
- command-line-of-sight
- CM
- countermeasures
- CO
- commanding officer
- co
- company
- coax
- coaxially mounted
- COLT
- combat observation/lasing team
- COMSEC
- communications security
- CONUS
- continental United States
- conventional unguided projectiles
- Any of a variety of unpropelled projectiles designed to follow a
ballistic path from launch to impact, deployment, or initiation of the lethal mechanism.
- cook off
- The functioning of a chambered round initiated by the heat of the weapon.
- CP
- (1) command post: A unit's headquarters from which command and control is centrally exercised.
- (2) concrete-piercing (fuze)
- CPB
- charged particle beam
- cruise missile
- An unmanned, self-propelled, guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift
for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.
- CS
- (1) combat support
- (2) chlorobenzaimalononitrile (riot control agent)
- CSS
- combat service support
- CVC
- combat vehicle crewman
D
- DCGE
- digital command guidance electronics
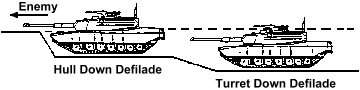
- defilade
- Protection from hostile observation and fire provided by an obstacle such as a hill, ridge, or bank.
- DEW
- directed energy weapon
- DIRCM
- defensive infrared countermeasures
- direct-fire range
- The maximum range of a weapon, operated in the direct-fire mode, at which the bullet's trajectory will not
rise above the height of the intended point of impact on the target. At this range, the gunner is not required to adjust for range in
order to aim the weapon. The comparable Russian term is point blank range.
- DoD
- (U.S.) Department of Defense
- DPICM
- dual-purpose improved conventional munitions
- DU
- depleted uranium
- DTIC
- (U.S.) Defense Technical Information Center
- DTV
- driver's thermal viewer
- DVE
- driver's vision enhancer
E
- EBFV
- engineer Bradley fighting vehicle
- ECCM
- electronic counter-countermeasures: That division of electronic warfare involving actions taken to ensure friendly effective use of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- ECM
- electronic countermeasures: That division of electronic warfare involving actions taken to prevent or reduce the effectiveness of enemy equipment and tactics employing or affected by electromagnetic radiations, and to exploit the enemy's use of such radiations.
- ELINT
- electronic intelligence
- ELRF
- eye-safe laser range finder
- EMP
- electromagnetic pulse
- emplacement
- (1) A prepared position for one or more weapons or pieces of equipment for protection from hostile fire and from which they can execute their tasks.
- (2) The act of fixing a gun in a prepared position from which it may be fired.
- EOD
- explosive ordnance disposal
- EPLRS
- Enhanced Position-Location Reporting System
- ERA
- explosive reactive armor
- ERDPICM
- extended range dual-purpose improved conventional munitions
- EW
- electronic warfare: That division of the military use of electronics involving actions taken to prevent or reduce an enemy's effective use of radiated electromagnetic energy, and actions taken to ensure our own effective use of radiated electromagnetic energy.
F
- FAAD
- forward area air defense
- FAASV
- field artillery armored support vehicle
- FAC
- forward air controller
- FAE
- fuel-air explosive (ammunition). This munition technology is employed in aerial bombs and artillery munitions,
and uses a dispersing explosive fill to produce intense heat, a longduration high-pressure wave, and increased HE blast area.
- FASCAM
- family of scatterable mines
- FAPDS
- frangible armor-piercing, discarding sabot (ammunition) - On impact with the target surface, the penetrator
breaks into several KE fragments. The round has Frag-HE effects with the higher velocity and flat trajectory of a sabot round.
- FCS
- fire-control system
- FCSW
- fire-control software
- FDC
- fire direction center: The element of a command post consisting of gunnery and/or communications personnel and equipment which receives target intelligence and requests for fire and converts it into appropriate fire direction and by which the commander exercises fire direction or fire control.
- FFAR
- folding-fin aerial rocket
- FIST
- fire support team: A group of field artillery observers with the required equipment to plan, request, coordinate, and direct fire support efforts for a company-sized maneuver force.
- fixed ammunition
- Ammunition in which the cartridge case (with propellant) is permanently attached to the projectile.
- FLIR
- forward-looking infrared radar
- FLOT
- forward line of own troops
- FM
- (1) frequency modulation
- (2) U.S. Army field manual
- FPF
- final protective fire(s): An immediately available, prearranged barrier of fire designed to impede enemy movement across defensive lines.
- fps
- feet per second
- FSU
- former Soviet Union
- ft
- foot; feet
- fuse
- A wick-type detonating device that, when lit by a match or other means, sets off the bursting charge of a projectile, bomb, or torpedo.
- fuze
- A mechanical or electrical detonating device that sets off the bursting charge of a projectile, bomb, or torpedo.
- FY
- fiscal year
G
- gal
- gallon(s)
- GCWR
- gross combination weight rating: vehicle curb weight + trailer weight + payload + fuel + crew and passengers.
- GHz
- gigahertz
- gm
- gram(s)
- GPS
- global positioning system
- gr
- grain(s)
- grenade
- A small explosive or chemical missile, originally to be thrown by hand, but now also to be
projected from special grenade launchers, usually fitted to rifles or carbines. Grenades may be classified as either
rifle or hand. Many variations of these have been used, including improvisations.
- GSR
- ground surveillance radar
- G/VLLD
- ground/vehicle laser locator designator
- GVWR
- gross vehicle weight rating: vehicle curb weight + payload + fuel + crew and passengers.
H
- H
- blister agent (mustard)
- HC
- hexachlorothane (smoke)
- HD
- blister agent (distilled mustard)
- HE
- high explosive
- HEAT
- high explosive anti-tank (ammunition)
- HEI
- high explosive incendiary (ammunition)
- HEI-T
- high explosive incendiary with tracer (ammunition)
- HEL
- high-energy laser
- HEMTT
- heavy expanded-mobility tactical truck
- HEP
- high explosive plastic (ammunition)
- HEP-T
- high explosive plastic with tracer (ammunition)
- HESH
- high explosive squash head (ammunition)
- HET
- heavy equipment transporter
- hit to kill
- A munition system incorporating integrated seeker, guidance and control, and fuze subsystems,
the warhead of which is initiated upon target impact or in close proximity thereto.
- HMMWV
- high-mobility multipurpose wheeled vehicle
- hotbox
- a box containing rounds of linked ammunition
- hp
- horsepower
- HQ
- headquarters
- HVAP-T
- hypervelocity, armor-piercing tracer (ammunition)
- hypervelocity
- Pertaining to velocities in excess of Mach 5.
- HUD
- head-up display
- Hz
- hertz
I
- IC3
- integrated communications, command, and control
- ICBM
- intercontinental ballistic missile
- ICM
- improved conventional munitions
- IFF
- identify friend or foe
- IFV
- infantry fighting vehicle
- in
- inch(es)
- indirect fire
- (1) Fire delivered at a target not visible to the firing unit.
- (2) Fire delivered to a target that is not used as the point of aim for the weapon or director.
- intravehicular
- within a vehicle
- intervehicular
- between vehicles
- INU
- inertial navigation unit
- IR
- infrared
- IRETS
- Infantry remoted-target system
- ISU
- integrated sight unit
- ITOW
- improved TOW
- IVIS
- intervehicular information system
J
- jet propulsion
- Reaction propulsion in which the propulsion unit obtains oxygen from the air, as
distinguished from rocket propulsion in which the unit carries its own oxygen-producing material. In connection with
aircraft propulsion, the term refers to a gasoline or other fuel turbine jet unit that discharges hot gas through a
tail pipe and a nozzle, which provides a thrust that propels the aircraft.
K
- KE
- kinetic energy: Class of ammunition which transfers energy to the target for the lethal mechanism. Ammunition types which employ KE include AP, APFSDS-T, and HVAP-T.
- kg
- kilogram(s)
- km
- kilometer(s)
- kph
- kilometer per hour
- kW
- kilowatts
L
- l
- liter(s)
- ladar
- Laser radar. Laser detection and ranging systems that use a laser light for detection of speed, altitude, direction, and range.
- lase
- To emit coherent light; to use a device or weapon that employs a laser light.
- laser
- light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. An assembly of components which produce
both spatially and temporally coherent light that is amplified by the stimulated emission of radiation.
- LAV
- light armored vehicle
- lb
- pound(s)
- LBE
- load-bearing equipment
- LCAC
- landing craft, air cushion
- LCD
- liquid crystal display
- LE
- low explosive: An explosive that, when used in its normal manner, deflagrates or burns rather than
detonates. That is, the rate of advance of the reaction zone into the unreacted material is less than the velocity of
sound in the unreacted material. Low explosives include propellants, certain primer mixtures, black powder,
photoflash powders, and delay compositions.
- lidar
- Light detection and ranging systems that use a light beam in place of conventional microwave beams
for atmospheric monitoring, tracking, and detection functions.
- line of sight guidance
- Guidance by which the missile, warhead, or projectile is commanded to follow a
trajectory that will cause it to intercept a target in a direction defined by a target tracker. The method requires
two-way communication with the missile, warhead, or projectile either by means of an IR, RF, wire, or fiberoptic link.
- LMG
- light machine gun
- LOS
- line of sight
- LRF
- laser range finder
- Lt
- lieutenant
- LTC
- lieutenant colonel
- LWRS
- laser warning receiver system
M
- m
- meter(s)
- MANPADS
- Man-Portable Air Defense System
- MBT
- main battle tank
- MCD
- missile countermeasure device
- MCLOS
- manual command-to-line-of-sight
- MCWP
- U.S. Marine Corps Warfighting Publication
- mech
- mechanized
- mechanical time fuze
- A fuze with a clocklike mechanism controlling the time the fuze will function.
- METT-T
- mission, enemy, terrain, troops, and time available
- MG
- machine gun
- MHz
- megahertz
- mi
- mile(s)
- MICLIC
- mine-clearing line charge
- micro air vehicles
- Unmanned air vehicles that are extremely small.
- mil
- A unit of measure for angles that is based on the angle subtended by l/6400 of the circumference of a circle.
- MILES
- Multiple Integrated Laser-Engagement System
- mine
- An encased explosive or chemical charge designed to be positioned so that it detonates when its
target touches or moves near it or when touched off by remote control. General types are land and underwater.
- MIRV
- multiple independently targeted reentry vehicle
- MLRS
- multiple launch rocket system
- mm
- millimeter(s)
- MMS
- mast mounted sight
- MoD
- Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom)
- MOPP
- mission-oriented protective posture
- MOUT
- military operations on urbanized terrain
- mph
- mile(s) per hour
- MRL
- multiple rocket launcher
- MT-LB
- A vehicle made by the former Soviet Union.
- muzzle velocity
- The velocity of a projectile at the instant the projectile leaves the muzzle of the weapon.
N
- NA
- N/A
- not applicable
- NBC
- nuclear, biological, chemical
- NCO
- noncommissioned officer
- NLW
- nonlethal weapon
- NOD
- night observation device
- NSN
- U.S. National Stock Number: The first four numbers are always the Federal Supply Classification (FSC) to which the item belongs. The FSC is followed by the National Item Identification Number (NIIN) which consists of a two-number code identifying the country of manufacture and a seven-number item identification. Each item has a different NIIN.
Example: M109A6 Paladin (NSN 2350-01-305-0028). 23 = Motor Vehicles, Trailers, and Cycles group. 50 = Combat, Assault, and Tactical Vehicles, Tracked class. 01 = USA country code. 305-0028 = item identification number.
- NVG
- night-vision goggles
- NVS
- night-vision system
O
- obscurants
- Any gas, liquid, or solid particle, either man-made or natural, suspended in the atmosphere
that affects any part of the electromagnetic spectrum by scattering, absorption, radiance, reflection, or refraction.
- obturator
- The rubber seal that helps the rotating band seal the propellant gas behind the projectile.
- OCM
- optical countermeasures
- ogive
- The curved forward part up to and including the tip of the projectile. Also called the head.
- OP
- observation post: A position which possesses the appropriate communications and other equipment to make military observations and from which fire is directed and adjusted onto targets.
- OPFOR
- opposing force
- OPSEC
- operations security
P
- passive armor
- A protective device designed to absorb or deflect the energy from an antiarmor warhead.
- passive homing
- A mode of guidance in which the direction is obtained from signals emitted by the target
without the necessity for illuminating or interrogating the target with an external signal.
- passive system (sensors)
- A sensor system that does not use emitted energy, but relies upon signals
emitted by its intended target. Forms of passive sensors common in military use include acoustic, gravimetric,
seismic, magnetic, radio frequency, microwave and millimeter wave, and optical (including IR, visible, and UV).
Such sensors are used for target detection, identification, and localization to support a wide range of military
functions including surveillance, fire control, and weapon fuzing.
- PB
- particle beam
- PBX
- plastic-bonded explosive
- PC
- personnel carrier
- PD
- point-detonating (ammunition fuze type)
- PEWS
- platoon early warning system
- PFC
- private first class
- PGM
- precision-guided munition: A munition equipped with a sensor that interacts with its aerodynamic control
surfaces and falls into one of the following categories: "guided," "smart," or "brilliant."
- PGS
- precision gunnery system
- PH
- probability of hit
- PH
- probability of hit
- pintel
- Post attached to a firing point or vehicle.
- PLGR
- precision lightweight GPS receiver
- plt
- platoon
- POE
- point of entry
- point-detonating fuze
- A fuze that functions immediately upon impact.
- POL
- petroleum, oils, and lubricants
- POS-NAV
- position-navigation
- proximity fuze
- A fuze designed to function when activated by an external influence such as the close vicinity of the target.
- psi
- pound(s) per square inch
Q
R
- RAAMS
- remote antiarmor mine system
- radar
- radio detecting and ranging
- RAM
- (1) radar absorbing materials
- (2) random access memory
- RAP
- rocket-assisted projectile
- RATELO
- radiotelephone operator
- RCS
- radar cross section
- RDF
- (1) radio direction finding: Radio location in which only the direction of a station is determined by means of its emission. Since this technique can be used against all electronic emitters, it is sometimes simply referred to as direction finding (DF).
- (2) rapid deployment force
- RDX
- cyclotri-methylenetrinitramine
- ready rounds
- rounds available for use on a weapon, whether in autoloader or in nearby stowage, which can be loaded within the weapon's stated rate of fire.
- REMS
- remotely employed sensor
- RHA
- rolled homogeneous armor: Often used as a standard armor hardness for measuring penetration of anti-tank munitions.
- riot control agents
- Substances which in low concentrations produce temporarily irritating or disabling
physical effects that disappear within minutes of removal from exposure. There is minimal risk of permanent injury,
and medical treatment is rarely required. (
- ROE
- rules of engagement
- ROF
- record of fire
- round
- (1) All parts that make up the ammunition necessary to fire one shot.
- (2) One shot expended by a weapon.
- ROV
- remotely operated vehicle
- RPG
- rocket-propelled grenade
- RPV
- remotely piloted vehicle
- RPVTS
- remotely piloted vehicle-target system
- RSTA
- reconnaissance, surveillance, and target acquisition
S
- SACLOS
- semiautomatic command-to-line-of-sight
- SAR
- (1) search and rescue
- (2) synthetic aperture radar
- SAM
- surface-to-air missile
- SAPHEI-T
- Semi-armor-piercing high explosive incendiary with tracer (ammunition)
- SAW
- squad automatic weapon
- scramjet
- supersonic combusion ramjet
- semi-active guidance
- Missile or warhead guidance in which the target is illuminated by an auxiliary
emitter (e.g., a laser or radar beam) and the missile or warhead homes in on the signal (reflection) from the target.
- semifixed ammunition
- The cartridge case is not permanently fixed to the projectile, so that zone charges
within cases can be adjusted to obtain desired ranges, but each round is inserted into a weapon as a unit.
- sensor
- Any equipment which detects and may indicate and/or record objects and activities by means of
energy or particles emitted, reflected, or modified by objects.
- sentient (or correlated)
- A type of "brilliant" munition that is aware of itself and its
surroundings; for example, a brilliant munition that responds to its environment, or communicates with others among
the same payload or salvo to seek out the targets and maximize interception.
- SEP
- spherical error probable or sphere of equal probability: A measure of accuracy at a specific range,
expressed in terms of the radius of a sphere, centered on the target, in which 50% of the payloads impact.
- SLAR
- side-looking airborne radar
- smart munition
- A "many-on-many" munition with target selection capability that does not require
an operator in the loop.
- SP
- self-propelled
- SFC
- sergeant first class
- SGT
- sergeant
- shaped-charge
- A type of explosively driven penetrator characterized by a relatively deep initial liner
shape which forms a narrow hypervelocity jet. The ballistic properties of the jet are such that the warhead must be
initiated within a few warhead diameters of the intended target to be effective.
- SHORAD
- short-range air defense
- SINCGARS
- single-channel ground and air radio subsystem. single-channel ground and airborne radio subsystem
- SITREP
- situation report
- SOP
- standing operating procedures
- SPLAT
- spray lead at target
- SRBM
- short-range ballistic missile
- SSG
- staff sergeant
- ST
- U.S. Army special text, student text
- STC
- slew-to-cue
- STOL
- short takeoff and landing
- stowed rounds
- Rounds available for use on a weapon, but stowed and requiring a delay greater than that for ready rounds (and cannot be loaded within the weapon's stated rate of fire).
- sustained rate of fire
- The actual rate of fire that a weapon can continue to deliver for an indefinite length of time without seriously overheating.
- sustainer
- A propulsion system that travels with, and does not separate from, the missile. Usually applied
to a rocket motor or rocket engine when used as the principal propulsion system - as distinguished from an auxiliary
system, such as the JATO unit.
T
- TACMS
- tactical missile system
- TACOM
- (U.S. Army) Tank-Automotive and Armaments Command
- TARDEC
- (U.S. Army) Tank Automotive Research, Development, and Engineering Command
- TAS
- target-acquisition system
- TBM
- theater ballistic missile
- TBMD
- theater ballistic missile defense
- TC
- (1) tank commander
- (2) U.S. Army training circular
- tear gases
- Gases which produce temporarily irritating or disabling effects which disappear within minutes of removal from exposure.
- terminal guidance
- terminal homing
- A procedure taken at the end of a vehicle or weapon's
trajectory, generally in response to direction from on-board sensing devices, to produce an end-game geometry such
that weapon lethality is maximized.
- tetryl
- trinitro-phenylmethylnitramine
- THAAD
- theater high-altitude area defense
- thermite
- Incendiaries that are a mixture of powdered iron oxide, powdered aluminum, and other materials.
- time on target
- A restrictive command that allows the fire direction officer or fire direction center to control the time the rounds will impact at the target.
- TIS
- thermal imaging system
- TM
- technical manual
- TNT
- trinitrotoluene (explosive)
- TOE
- table(s) of organization and equipment: A document which prescribes the normal mission, organizational structure, personnel, and equipment requirements for a military unit and is the basis for an authorizations document.
- TOW
- tube-launched, optically-tracked, wire-guided (anti-tank missile)
- TPDS-T
- target practice discarding sabot with tracer (ammunition)
- TP-T
- target practice with tracer (ammunition)
- tracer
- An element inserted in the base of projectiles that, when ignited, burns and allows both the projectile's trajectory and the impact to be observed during flight.
- TRADOC
- (U.S. Army) Training and Doctrine Command
- TTS
- tank thermal sight
U
- UCAV
- uninhabited combat air vehicle
- UAV
- unmanned aerial vehicle. unmanned air vehicle
- UK
- United Kingdom
- US
- United States
- USMC
- United States Marine Corps
- UV
- ultraviolet
- UXO
- unexploded ordnance
V
- VEESS
- vehicle engine exhaust smoke system
- VETRONICS
- vehicle electronics
- VSHORAD
- very short-range air defence
- VT
- variable-timed
- VTOL
- vertical takeoff and landing
- VX
- chemical nerve agent (persistent)
W
- warhead
- That portion of a rocket or guided missile that contains the load that the vehicle is to deliver.
It may be empty or contain high explosives, chemicals, instruments, or inert materials. It may also include a booster,
fuze(s), adaption kits, and/or burster(s).
- way point
- An intermediate point on a route or line of travel.
- WMD
- weapons of mass destruction: Weapons that are capable of a high order of destruction and/or of being
used in such a manner as to destroy large numbers of people. Weapons of mass destruction can be high explosives or
nuclear, biological, chemical, and radiological weapons, but exclude the means of transporting or propelling the
weapon where such means is a separable and divisible part of the weapon.
- WP
- white phosphorus
- WWI
- World War I
- WWII
- World War II
X
Y
- yd
- yard(s)
Z
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
