First introduced in 1967, the BMP (
Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty) represents a transition from the "armored personnel carrier" to the "infantry combat vehicle" in the Soviet and most Warsaw Pact armies.
It has replaced the BTR-50P and complements the BTR-60PB in first-line motorized rifle units.
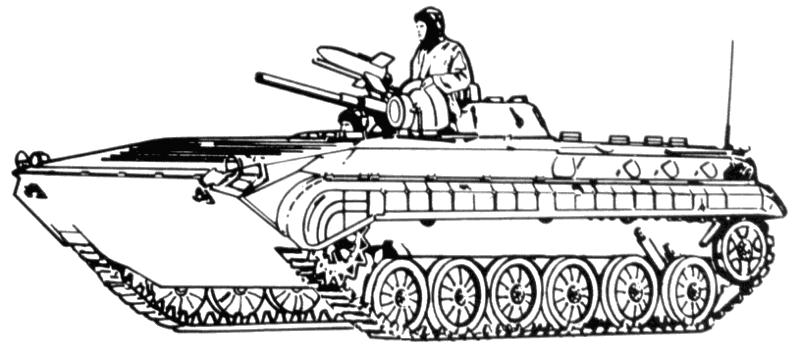
The BMP-1 has an all-welded hull and a three-man crew with the driver seated at the front left, the commander to his rear and the gunner at the turret.
To the rear of the turret are four large hatches in the roof of the troop compartment; two large exit doors are also in the rear.
There are four firing ports in each side of the troop compartment and one in the left rear door.
The BMP has an infrared searchlight, periscopes, and sights for night operations.
It also has a capability to make its own smoke screen by injecting diesel fuel into the exhaust manifold.
The vehicle is amphibious, being propelled through the water by its tracks.
The BMP has relatively thin armor, with a maximum thickness of 19 millimeters in the hull and 23 millimeters in the turret.
This provides protection against .50-caliber armor-piercing rounds only over the 60° frontal arc.
The vehicle is extremely vulnerable to ATGM and tank fire.
Its compactness dictates the location of critical areas in such a manner that penetration anywhere on the vehicle will normally result in a mobility, fire-power, or personnel kill.
These critical areas include the engine compartment and ammunition storage area, on the right side; fuel cells in the rear doors; and the troop compartment.
Because of its limited capability to depress the main gun, the BMP cannot engage tanks and APCs from good hull-down positions.
It is thus very vulnerable to enemy fire when it exposes itself to engage targets.
Although the turret can traverse 360°, the main gun and coaxial machine gun must be elevated to clear the IR searchlight on the commander's cupola.
This creates a dead space for both weapons between 10:00 and 11:00 o'clock.
The BMP can maintain its top speed of 65 kilometers per hour for only short periods of time.
This results from the high amount of vibration and the possibility of transmission failure.
Due to the complicated loading mechanism and the lack of stabilization, the 73mm gun or the coaxial machine gun cannot fire accurately on the move over rough terrain.
The BMP must be stationary when firing and tracking an ATGM.
The SAGGER is difficult to reload; it cannot be reloaded at all under NBC conditions without breaking the integrity of the vehicle's protective overpressure system.
To reload the SPIGOT and SPANDREL, the gunner must open his hatch; this, again, negates the overpressure system and exposes him to fire.
The land navigation system must be zeroed every 30 minutes.
Other options are improved tracks, smoke grenade launchers, laser warning receivers, spall liners, air conditioning, and a more powerful engine (360 hp).
A French SNPE explosive reactive armor (ERA) kit and others are available for use on the BMP-1. However, during dismounted troop movement, ERA would be a hazard. Thus, passive armor is
more likely; and ERA application is doubtful. Additional armor application may jeopardize amphibious capability.
Russian BMP-2 2-man turrets with gun and fire control system are being marketed for BMP-1 customers. The Volgorod Tractor Plant offers the
BMP-1/B30 package with a B30 turret (a drop-in one-man turret with 2A42 30-mm gun, 7.62-mm coax MG, BMP-2-type fire control system,
PZU-8 AA sight, and a 9P135M ATGM launcher for AT-4/-5 ATGM). Russian KBP offers a drop-in one-man turret, called Kliver, with a stabilized
2A72 30-mm gun, a 4-Kornet ATGM launcher, thermal sights, and improved fire control system. A Ukrainian turret is also available.
Thermal gunner sights are available; however, most upgrades involve adding a thermal sight with an improved gun and improved fire control
system. The Russian Alis thermal gunner's sight is available. The Slovenian TS-F ATGM thermal night sight has a detection range of 4,500 m
and a recognition range of 2,000 m.
- BMP
- The prototype IFV. Not fielded.
- BMP-A
- Initial BMP production variant. Halted with insignificant numbers.
- BMP-1, Korshun, BMP Model 1970
- 1970. The baseline production infantry fighting vehicle.
Has an AT-3/SAGGER anti-tank guided missile.
Its most noticeable modifications are the lengthening of the bow and the extension of the deflector shroud to the rear.
These modifications were designed to improve the BMPs swimming capability, which was inhibited by the forward placement of the engine.
Other changes include improved fume venting, NBC protection, an enlarged/squared firing port for the PKM machine gun below the turret and repositioned vision blocks above the crew compartment.
A variety of variant IFVs/APCs and support vehicles have been developed using this chassis.
Copies include: Chinese WZ 501/Type 86, Czech BVP-1, and the Polish BWP-1.
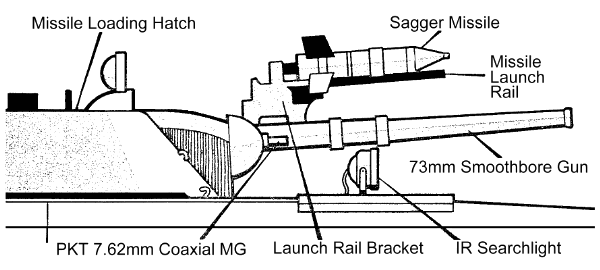 Recognition features:
Recognition features:
- Tracked vehicle.
- Six road wheels, evenly spaced, with three support rollers.
- Vertical lines on track skirts.
- Two bulging doors in rear.
- Four hatches on top of crew compartment.
- Four gun ports on left and right sides.
- Low silhouette with flat turret centered on hull.
- Sharp, sloping front with distinctive ridged surface.
- Commander's hatch mounts infrared searchlight.
- Amphibious.
- BMP-1K, BMP M1974
- Company command IFV, with added R-126 and R-107 transceivers.
Firing ports and most periscopes are blocked.
- BMP-1KSh, BMP M1978
- Former Soviet regiment or division command and staff vehicle, with turret mounted erectable 10-meter radio mast.
Radios include R-130, R-111, and R-173. BMP-1KShM variant has upgraded radios.
- No gun. "Hawkeye" antenna extends from front of turret.
- Antenna telescopes upward.
- Right rear side has tubular case for "Hawkeye" antenna parts.
- Rear center box-shaped generator.
- Four whip antennas on rear: two on left, two on right.

U.S. Army Photo
710x300, 79K, JPEG
- BMP-1M
- Iranian variant with drop rear gate vs double doors.
- BMP-1P
- 1974. See data above.
The BMP-1P upgrade is widely fielded, with an AT-4/-5 ATGM launcher replacing the BMP-1's AT-3 launcher. The vehicle also added
smoke grenade launchers. The AT-4/-4B ATGMs are less likely to be employed on this vehicle.
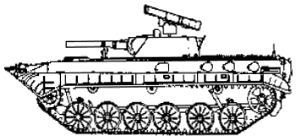
- BMP-1PG
- This Russian upgrade is similar to BMP-1P with an added AG-17 30-mm automatic grenade launcher and other options, including thermal sights.
- BMP-1PK
- Command variant, with addition of R-126 and R-107 transceiver.
A small telescoping antenna is mounted on right rear. Firing ports and telescopes on right side are blocked off.
- BMP-PPO
- This is a mobile training version.
The turret has been removed and the space normally occupied by the fighting and passenger compartments is used to provide eight student training stations.
Positions are also available for an instructor and a driver.
Each of the student stations has a hatch, observation devices, and communications equipment which duplicate those of a normal BMP commander's position.
- BMP-1TJ
- Finish armored tracked forward observation post vehicle.

800x536, 119K, JPEG

800x536, 156K, JPEG
Finnish Defence Forces Photos
- BPzV
- Czechoslovakian reconnaissance variant with a Tall Mike external tripod mounted radar.
- BREM-2
- Light recovery and repair vehicle with a light crane.
- BREM-4
- Armored recovery vehicle. Czech designation is VPV.
Uses the standard BMP-1 chassis, but with the turret removed and a rotatable crane added.
This crane reportedly assists in removing light vehicle turrets and engines.
- BRM-1, BMP-R, BMP M1976/1
- Reconnaissance command variant with improved sensors, "Tall Mike" battlefield surveillance radar, and low-profile 2-man turret.
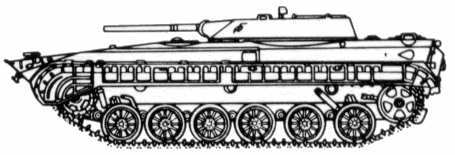
- BRM-1K, BMP M1976/2
- Improved version of the BRM-1.
- BRM-23
- Bulgarian reconnaissance variant with a 23-mm cannon, AT-3 ATGM, navigation system, NBC and artillery reconnaissance devices, and image intensifier night sights.
- IMR
- Armored engineer tractor, with crane and dozer blade.
- IRM
- Engineer underwater reconnaissance vehicle, with mine detectors and mapping capabilities.
- MLI-84
- Romanian APC variant with a 12.7-mm MG.
- MP-31
- Modernized command and staff vehicle.
- OT-90
- Czech APC variant with 14.5-mm and 7.62-mm MGs.
- PRAM-S
- Czechoslovakian self-propelled 120-mm mortar variant.
- PRP-3, BMP M1975
- Artillery reconnaissance vehicle.
The PRP-3 is easily distinguished from the BMP-1 by an enlarged two-man turret, which has been moved toward the rear and a 7.62mm machine gun rather than the 73mm gun and AT-3/Sagger of the BMP-1.
Also, a rectangular folding antenna for the "Small Fred" battlefield surveillance radar is mounted on the rear of the turret.
The effective range of the radar is 20 kilometers.
The PRP-3 carries a five-man crew and extensive radio and optical equipment.
- Single 7.62mm machine gun set in small ball in front of turret.
- Navigation: 1G25 gyrocompass and 1G13 gyro course indicator.
- Fire direction: 1V520 ballistic computer.
- 1RL126 Small Fred radar mounted on rear of turret.
- 1PN61 night vision sensor and 1D11 laser rangefinder on right side of turret.
- No sensors on left side of turret.
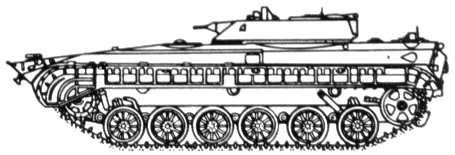
- PRP-4
- Artillery reconnaissance vehicle. A development of the PRP-3.
- Single 7.62mm machine gun set in small ball in front of turret.
- Navigation: 1G25-1 gyrocompass and 1G13 gyro course indicator.
- Fire direction: 1V520 ballistic computer.
- 1RL133M-1 Tall Mike battlefield surveillance radar mounted on rear of turret.
- 1PN61 (PRP-4M has improved 1PN71) night vision sensor and 1D11M-1 laser rangefinder on right side of turret.
- 1PN59 thermal imaging night vision device and 1D14 laser rangefinder on left side of turret.

PRP-4
U.S. Army Photo
753x560, 99K, JPEG
- Snezka
- Czech stretched version battlefield surveillance vehicle, with a sensor suite (including radar) mounted on a telescoping arm.
- SVO
- Czechoslovakian turretless mine clearing variant with 24 large rocket-propelled line charges.
- VP90
- Czech reconnaissance vehicle with 14.5 and 7.62-mm MGs.

BMP-1
14-NOV-1984
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x510, 131K, JPEG

Damaged BMP-1
01-MAY-1974
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x680, 235K, JPEG
BMP-1. On display at Bolling Air Force Base. 01-OCT-1986. U.S. DoD Photos

1024x400, 124K, JPEG

1024x490, 127K, JPEG

1024x674, 122K, JPEG
Finish BMP-1. Finnish Defence Forces Photos

800x533, 102K, JPEG

800x533, 111K, JPEG

800x533, 65K, JPEG

800x533, 129K, JPEG

800x533, 137K, JPEG

800x533, 100K, JPEG

Damaged Iraqi Republican Guard BMP-1
Operation Desert Storm
28-FEB-1991
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x679, 171K, JPEG

Iraqi Army BMP-1
Coalition checkpoint in Tarmiya, Iraq
25-MAR-2006
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x731, 260K, JPEG
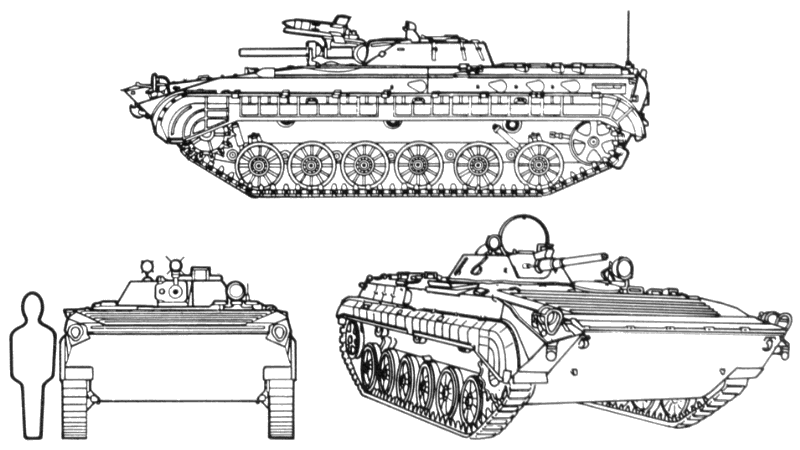

 Recognition features:
Recognition features:



