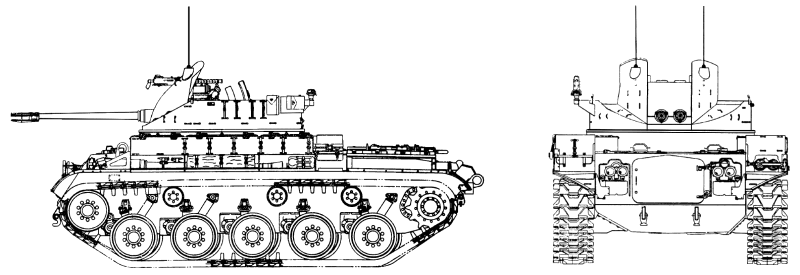
| GENERAL DATA |
|---|
| | M42 |
|---|
| Alternative Designations | Duster |
|---|
| Country of Origin | USA |
|---|
| Role | Low-level air defense, ground support |
|---|
| Date Of Introduction | 1953 |
|---|
| Crew | 4-6 (commander-radio operator, driver, gunner, squad leader, 2 cannoneers) |
|---|
| Combat Weight | 24.90 tons (22.59 mt) |
|---|
| Ground Pressure | 9.1 psi (0.64 kg/cm²) |
|---|
| Length, Overall |
20.85 ft (6.36 m) |
|---|
| Length, Hull |
19.08 ft (5.81 m) |
|---|
| Width, Overall |
10.58 ft (3.23 m) |
|---|
| Height, Turret Top |
9.41 ft (2.87 m) |
|---|
| Ground Clearance | 17.3 in (440 mm) |
|---|
| PERFORMANCE |
|---|
| | M42 |
|---|
| Engine | Continental AOS-895-3 500 hp (373 kw) 6-cylinder, air-cooled, supercharged gasoline.
M42A1: AOSI-895-5 with fuel injection. |
|---|
| Transmission | CD 500-3 cross drive |
|---|
| Range | 100 miles (161 km). M42A1: 120 miles (193 km) |
|---|
| Fuel Capacity | 140 gal (530 l) |
|---|
| Road Speed | 45 mph (72 km/h) |
|---|
| Cross Country Speed | 25 mph (40 km/h) |
|---|
| Swim Speed | N/A |
|---|
| Fording Depth | 4 ft (1.22 m) |
|---|
| Grade | 60% |
|---|
| Side Slope | 30% |
|---|
| Trench Crossing | 6 ft (1.83 m) |
|---|
| Vertical Wall Climb | 2.33 ft (0.711 m) |
|---|
| PROTECTION |
|---|
| | M42 |
|---|
| Armor | Rolled and cast homogenous steel: 0.3 - 1.25 in (7.62 - 31.75 mm) |
|---|
| Applique Armor | N/A |
|---|
| Explosive Reactive Armor | N/A |
|---|
| Active Protective System | N/A |
|---|
| NBC Protection System | N/A |
|---|
| Smoke Equipment | N/A |
|---|
| ARMAMENT |
|---|
| M42 |
|---|
| Type |
Mount |
Typical Ammo Load |
| 40mm M2A1 dual automatic gun |
Turret - M4E1; 7 round hopper manually loaded by 4 round clips |
480.
HE-T SD, HEI-T SD, AP-T |
| .30 caliber M1919A4 (replaced by M60) light machine gun |
Turret right front; flexible; belt-feed |
1,750. |
|
| FIRE CONTROL |
|---|
| | M42 |
|---|
| Fire Control System | M38 computing sight, M24C reflex sight, speed ring sights |
|---|
| Main Gun Stabilization | N/A |
|---|
| Rangefinder | N/A |
|---|
| Infrared Searchlight | Available |
|---|
NOTES
The M42 Duster (a member of the
M41 Walker Bulldog family of armored vehicles) is a full-track-laying, lightly armored, anti-aircraft vehicle designed for use with maneuver forces against very-low to low-altitude subsonic air attack.
Because of its rapid rate of fire, the vehicle's 40mm dual automatic gun proved to be effective as a support weapon against ground targets.
The interior of the M42 is divided into three areas: driving compartment at the front, stowage compartment in the center, and engine compartment in the rear.
The driving compartment contains the driving controls and instruments.
The seats for the driver (front left) and commander-radio operator (front right) are in the driving compartment.
The stowage compartment serves as a base for the gun mount and has stowage space for 12 boxes of 40mm ammunition.
The engine compartment houses the main engine, auxiliary generator and engine, transmission, and fuel tanks.
The M13 periscope is used by the driver and commander while operating under combat conditions during daylight, and the M19 periscope (a binocular-type, enlarged-view device) is used when the vehicle is being driven under blackout conditions.
Infrared light is projected forward from the blackout headlights to illuminate the field of view.
The M19 periscope converts the infrared image to a visible image which is viewed through conventional eyepieces.
The communications system of the M42 consists of a radio set (AN/VRC-7,8,9, or 10), a radio receiving set (AN/GRR-5), an intercommunications set (AN/UIC-1, replaced by AN/VIC-1), and interphones.
This equipment is shock-mounted on support shelves in the driving compartment.
The AN/VRC is used for intervehicular and command communication, and the AN/GRR-5 provides air defense intelligence.
The welded armorplate gun mount is an open-topped cylinder in the center section of the vehicle.
This mount, supported on a ball bearing race ring, can be traversed 360° in either direction by power (9 seconds) or manually (10.30 per crank revolution).
Crew positions for the squad leader (left), gunner (right), and two cannoneers (rear) are in the gun mount.
The squad leader commands, via the intercommunications set, either from the commander's seat or the gun mount.
The M42 is not suited to airmobile operations primarily because it is not helicopter-transportable.
The M42 is suitable for airborne operations, but it is not not air-droppable and must be air-landed.
The M42 replaced the WWII M19 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun in U.S Army service and was replaced by the Vulcan and Chaparral systems.
HISTORY
- Military characteristics of the T141 self-propelled twin 40mm gun are approved November 1950.
- Design, development, manufacture, and test are authorized August 30, 1951 for:
- T141 interim anti-aircraft vehicle.
- T141E1 ultimate anti-aircraft vehicle.
- T53 radar fire control vehicle.
- Cleveland Tank Plant, operated under Government Contract DA-2O-O89-ORD-2931 by Cadillac Motor Car Division, GMC, is designated design and production agency for the vehicle.
In addition, ACF Industries, Inc., Berwick, Pa., is designated a prime contractor under Government Contract DA-36-O34-ORD-91.
- The first Cadillac produced vehicle is Ordnance accepted in August 1951.
- The first ACF vehicle is Ordnance accepted in April 1952.
- The T141E1 and T53 vehicles are canceled May 9, 1952 due to excessive complexity, development time, and cost.
The Light Antiaircraft Development Program, begun in 1952, includes a proposed "Raduster" improvement (a Duster with a range-only radar).
- Serious vehicle operating difficulties accompanying the use of 1/2" side armor,
leads to the conclusion in April 1953 that 3/4" side armor should be adopted.
Subsequent engineering studies and extensive tests on production techniques and modifications
prove the feasibility of 1/2" side armor which is re-adopted early in 1954 and standardized.
- Tests of early production T141 vehicles lead to a revised set of military characteristics which are approved September 9, 1953 at the Cleveland Tank Plant
after incorporating 37 mandatory modifications on all previously produced vehicles.
- The M42 (T141) is classified as Standard Type and the M19A1 is classified as Limited Standard Type on October 22, 1953.
- ACF Industries M42 production terminates in December 1953.
- M42 military characteristics are revised May 6, 1954 as standard with either 1/2" or 3/4" side armor.
- The M42A1 (with fuel-injection engine) is classified as Standard Type and the M42 is classified as Limited Standard Type on February 2, 1956.
- The Raduster program is changed in June 1956 to provide for development of the improved T50 anti-aircraft fire control system to a production standby status for use with the Duster in the event of an unforeseen emergency.
- The proposed Raduster improvement program is abandoned in February 1958 after engineering and user tests indicated only marginal improvements in effectiveness over the standard M42.
- Cadillac M42A1 production terminates in December 1959.
Cadillac and ACF Industries have produced total of 3,700 M42/M42A1 vehicles during the system's production run.
- The M42 system continues in U.S. Army service until the early 1960s, when it is transferred to the Army National Guard.
- In 1965, Army National Guard M42A1 gun batteries are overhauled and activated for use in Vietnam.
The Dusters are intended to be a temporary force until Vulcan and Chaparral systems are available,
but in December 1965 the activation is extended to allow phase-in of Vulcan/Chaparral.
- In late 1966, the Dusters begin arriving in Vietnam:
- 1st Battalion, 44th Artillery (Automatic Weapons, Self-Propelled), supporting the 3d Marine Division in northern I Corps.
- 5th Battalion, 2d Artillery (Automatic Weapons, Self-Propelled), assigned to II Field Force Artillery in II Corps.
- 4th Battalion, 60th Artillery (Automatic Weapons, Self-Propelled), assigned to 41st Artillery Group, I Field Force Artillery, in III Corps.
- In 1971 the Army begins to withdraw its air defense units from Vietnam. By the middle of 1972 the Dusters have been withdrawn and returned to Army National Guard service.
- The M42 system is retired from Army National Guard service in 1988.
AIR DEFENSE DESIGN
The M42 defense design is based on a low altitude or dive attack by a 520-knot maneuvering aircraft approaching from any direction.
Defense design factors:
- Maximum effective range - 1,650 meters.
- Rate of fire - 240 rounds per minute (120 per barrel).
- Maximum mutual support distance - 1,100 meters.
- Minimum mutual support distance - 100 meters.
AIRCRAFT ENGAGEMENT SEQUENCE
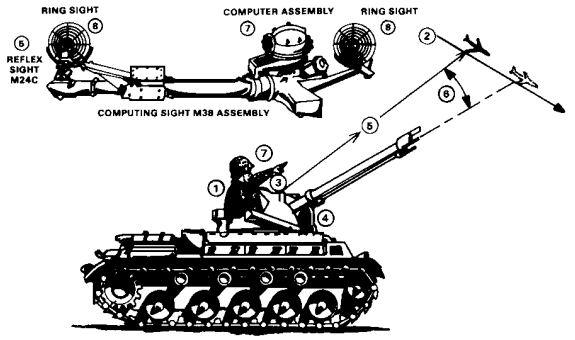
The Duster engagement sequence begins when the squad leader (1) designates the target, estimates target speed, direction of flight, and the angle of dive or climb, (2) and sets these values into the M38 computing sight (8).
The gunner (3) engages the power drive mechanism and traverses the gun mount and elevates the dual 40mm guns (4) until the target is centered in the reticle of the M24C reflex sight (5).
The sight mechanically computes the lead angle (6) based on target speed and flight direction; super-elevation is automatically inserted based on gun elevation.
When target tracking is steady, the gunner reports, "ON."
Upon receiving the report, "ON," and having determined that the target is within range, the squad leader commands, "FIRE."
The gunner commences firing and continues to fire, while the gun is hand-fed by the loaders, until the target is destroyed or the squad leader commands, "CEASE FIRING."
The normal mode of firing is that of POWER CONTROL, using the M38 computing sight.
An alternate mode of operation is that of MANUAL.
In this latter mode, the mount and dual gun are moved in azimuth and elevation by hand-operated cranks.
When operated in the MANUAL mode, speed ring sights (8) are used for fire control.
GROUND SUPPORT
The Duster can deliver a high volume of accurate direct fire against enemy personnel, lightly armored vehicles, bunkers, observation posts, crew-served weapons, and similar targets.
Indirect fire also may be used, although it is less effective and is worthwhile only in a rather narrow range of circumstances.
Limitations of the M42 in the ground support role include its high silhouette, lack of overhead crew protection, and ineffectiveness against heavily armored vehicles.
Due to these limitations, the M42 must not be employed in a tank role or as a self-propelled anti-tank weapon.
SIGHTS
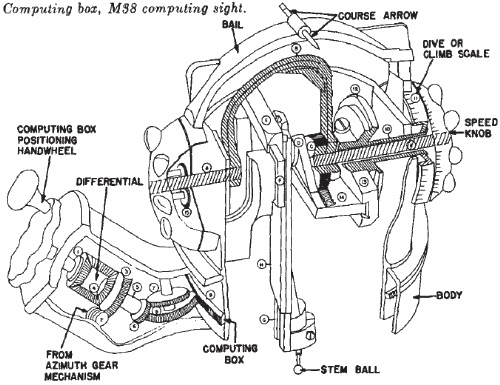
The
M38 computing sight is the M42's primary means of fire control.
It consists of a computing box, two speed knobs with two speed scales graduated from 0 to 700 miles per hour on each knob, a target course arrow mounted on top of a bail, a computing box positioning handwheel,and a main support bar for housing a steel band used to transmit lateral motion to the gunner's M24C reflex sight.
The
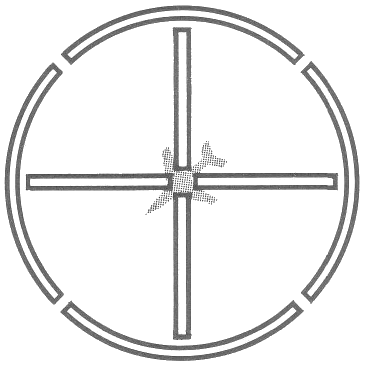
M24C reflex sight has a light window, reticle and mirror, magnifying lens, and coated glass reflector.
The M24C is designed to superimpose a reticle pattern in the gunner's line of sight and is used in conjunction with the M38 computing sight during power operation.
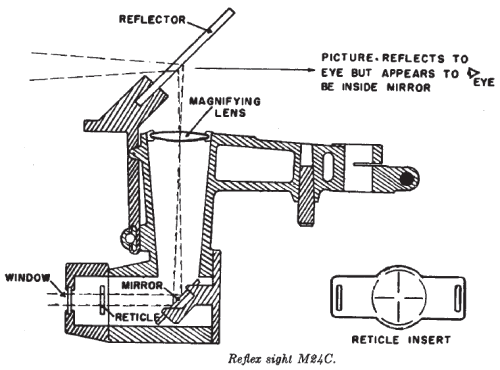
The
speed ring sight is used during manual operation if a power failure or local control system malfunction occurs.
It has a rear peep element and a series of eight concentric circles as a front element.
The eight circles represent the required lead, at a midpoint range of 1,000 yards, for a target traveling 25, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 or 700 miles per hour.
The rear peep element can be adjusted up, down, left, or right.
M2A1 40MM GUN
Main armament is the M2A1 dual 40mm automatic gun (Swedish Bofors L/60).
The 40mm gun is a high-velocity, flat-trajectory, clip-fed, automatic-loading weapon capable of firing 240 rounds per minute (120 per barrel).
The cyclic functioning of each gun is automatic from the firing of one round to the next.
The 40mm gun may be either fully automatic or semi-automatic.
It is air-cooled and, if fired at maximum rate, will over-heat after about 100 rounds are fired.
When over-heated, firing must be suspended and the barrel changed, which takes approximately 3 minutes.
Gun tube life can vary from 4,000 to 16,000 rounds, depending on the amount of overheating due to continuous firing.
The extreme deterrent range is the tracer burn-out range of projectiles.
At this range, the fire is inaccurate but, if delivered with maximum density, may cause enemy aircraft to take evasive action, break formation, and even abandon their mission.
Extreme deterrent range for the 40mm gun is 3,500 to 5,500 yards (3,200 to 5,029 m).
The maximum effective range is the maximum distance within which the gun may be expected to fire accurately and inflict casualties or damage.
It depends on tracer observation, but in addition, is determined by the type of sighting device, lead tolerance, angle of approach, and the average state of personnel training.
The maximum effective range for the 40mm gun is 1,800 yards (1,650 m).
The shortest range at which the gun can track a target depends on target speed and the maximum tracking rate of the gun mount.
The M42 can track a 600 mph (966 kph) target at approximately 420 yards (384 m) minimum range.
Other characteristics of the M2A1 gun on M4E1 mount:
- Traverse limits: 360°
- Elevation limits, powered: -3° to 85°
- Elevation limits, manual:-5° to 87°
- Elevation slew rate: 25°/sec
- Azimuth slew rate: 40°/sec
AMMUNITION
M25 Dummy Cartridge
Length: 17.60 in (447 mm)
Weight: 4.75 lb (2.15 kg)
Color Identification: Black with white markings
M81, M81A1 Armor Piercing with Tracer (AP-T)
Used against aerial targets, lightly armored vehicles, concrete shelters, and similar targets.
The AP-T round has no fuze.
Length: 17.60 in (447 mm)
Weight: 4.58 lb (2.08 kg)
Color Identification: Black with white markings
Horizontal Range: 9,475 yds (8,664 m)
M91 Target Practice with Tracer (TP-T)
Length: 17.60 in (447 mm)
Weight: 4.72 lb (2.14 kg)
Color Identification: Blue with white markings
MK2 High Explosive with Tracer, Self Destroying (HE-T SD)
Used against aerial targets, personnel, and light materiel.
The HE-T shells have a supersensitive fuze which bursts on contact.
If no contact is made as the tracer burns out, the relay ignition charge is ignited detonating the bursting charge of the shell.
Length: 17.60 in (447 mm)
Weight: 4.75 lb (2.15 kg)
Projectile Weight: 1.985 lb (0.9 kg)
Color Identification: Olive drab with yellow markings
Muzzle Velocity: 2,870 fps (875 mps)
Vertical Range: 5,100 yds (4,663 m)
Horizontal Range: 5,200 yds (4,755 m)
Tracer Burn Time: 7-12 seconds
Mk2 High Explosive Incendiary with Tracer, Self Destroying (HEI-T SD)
Used against aerial targets, personnel, and light materiel.
The HEI-T shells have a supersensitive fuze which bursts on contact.
If no contact is made as the tracer burns out, the relay ignition charge is ignited detonating the bursting charge of the shell.
Length: 17.60 in (447 mm)
Weight: 4.75 lb (2.15 kg)
Color Identification: Olive drab with yellow markings
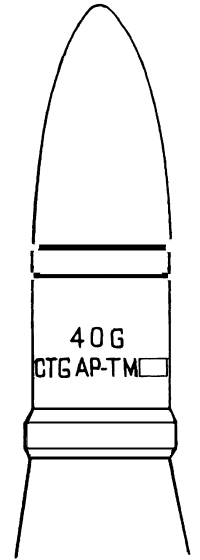
M81A1 AP-T
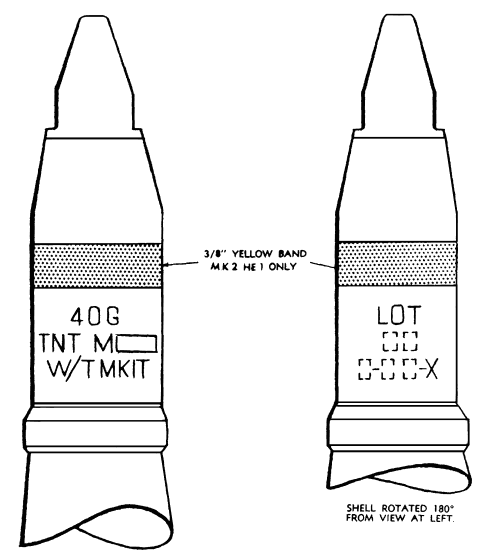
M25, M91, Mk2
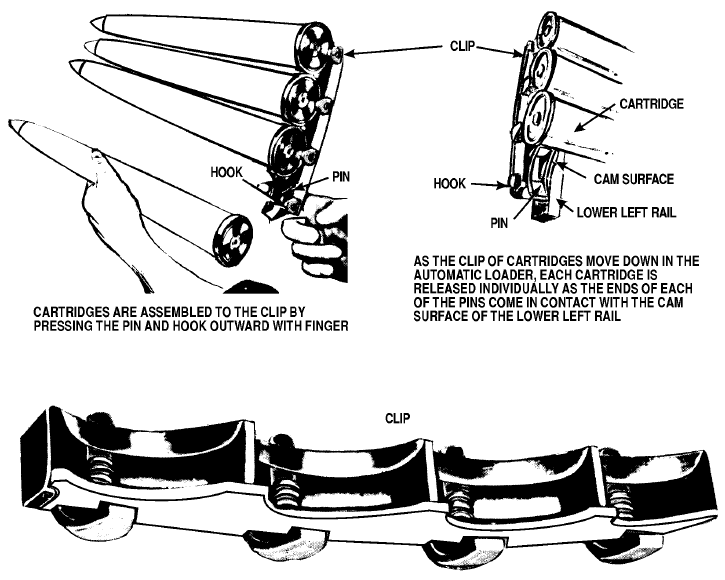
Loading 40mm charger clips
VARIANTS
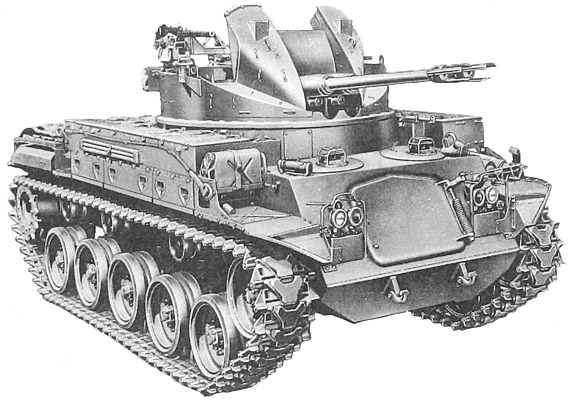
- M42, T141
-
1953. "Gun, Twin 40mm, Self-Propelled, M42", "Gun, Self-Propelled, Full Tracked, Twin 40mm, M42".
Original production model. Replaced the WWII M19 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun.
- M42A1
-
1956. "Gun, Twin 40mm, Self-Propelled, M42A1", "Gun, Self-Propelled, Full Tracked, Twin 40mm, M42A1".
A fuel injection system was designed for the M42's engine to improve fuel economy and to increase vehicle range by 20%.
This resulted in standardizing the M42A1 with the AOSI-895-5 fuel injection engine and classifying the M42 as limited standard.

Exercise Brave Shield XIX.
Fort Hood, Texas.
15-MAR-1979
U.S. DoD Photo
1024x680, 244K, JPEG

Exercise Brave Shield XIX.
Fort Hood, Texas.
15-MAR-1979
U.S. DoD Photo
717x1024, 190K, JPEG

Duster used for target practice.
Melrose Air Force Range.
18-FEB-2009
U.S. Air Force photo
1024x645, 207K, JPEG